Cell cycle regulatory factor-Cyclic Dependent Kinase 1
Cell cycle is a series of ordered events that take place in a cell from the first division to the next one. Cell cycle can be divided in two phases: interphase and mitotic (M) phase. During mitotic phase (M phase) , a series of changes take place in cellular modality and structure, including division of nucleus, condensation of chromosomes, appearance of spindle and equal distribution of chromosomes to two daughter cells, genetically identical to each other. It is well known that there is a common mechanism to regulate the mitotic phase of the cell cycle in all the eukaryote cells from yeast to human. MPF, a protein kinase, can phosphorylate multiple proteins to change their structure and function. Thus it can regulate their ability in cell metabolism. Activated MPF is a heterodimeric protein composed of cyclin B and p34CDK2. p34CDK2 is encoded by the CDC2 gene and it has little kinase activity in the absence of its partner, cyclin. During the transition of G2 to M phase, p34CDK2 will bind to cyclin. Wee1/mik1 and CDK kinase phosphorylate the Thr-14, Tyr-15 and Tyr-161 residues in CDK. The MPF is activated after cdk1 is de-phosphorylated by cdc25c kinase. It is reported that this protein kinase complex plays a key role in the control of cell cycle and it is regarded as engine that can drive the cell cycle. p34CDK2 is also called Cyclin Dependent Kinase (CDK), there are 11 genes for CDKs encoding right now. Although different CDKs have distinct functions in different period of cell cycle, the levels of CDKs remain relatively constant throughout the cell cycle and the regulation is done by CDK phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. The periodic change in activity of CDK will mediate a series of reaction during cell cycle.
CDK1 (Cyclin Dependent Kinase 1) is a highly conserved serine-threonine kinase. And it is vital for regulating the progression through cell cycle. For human, CDK1 is encoded by CDC2 gene. The complex of CDK1 and cyclin can phosphorylate several substrates (over 75 proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and drive the cell cycle.
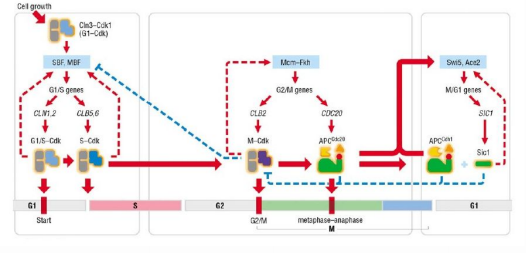
The regulatory function of CDK1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been clearly investigated since the CDK1 is highly conserved. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, there are two complex, SBF (SCB-binding factor) and MBF (MCB- binding factor), which control the start of the cell cycle. These two complexes can regulate the gene transcription during G1/S phase. And they are inactive under normal circumstances, as SBF is blocked by Whi5. After phosphorylation of Cln3-Cdk1, Whi5 is released from nuclear and the gene in G1/S phase is capable to be transcribed.
Equally, the regulation of CDK1 is highly involved in the whole cell cycle. This process is closely related to its partner, cyclin. Binding to the Cyclin can change the position of the active site to activate the CDK1. Besides, there is a conservative protein Kinase that can inhibit CDK1 by phosphorylation. Moreover, the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs) can interact with a CDK1-cyclin complex to control the commencing and ending of the cell cycle.
The CDK1 is vital for regulation of cell cycle. In view of that, we had done lots of work on this kinase. At first, the gene of CDK is obtained by reverse transcription and the protein is expressed in E.coli. The recombinant CDK1 (Catalog No.: RPB888Hu01) was purified by affinity chromatography and the purity is over 95%, the purity of the protein is shown in Figure 2 (MV=13.5KD). The Antiserum is collected from rabbits which are immunized by purified recombinant CDK1. The polyclonal antibody (Catalog No.: PAB888Hu01) specific for CDK1 is purified from the antiserum by affinity chromatography.
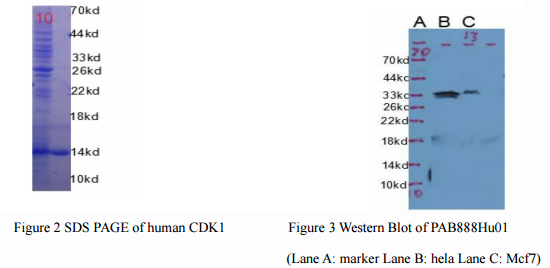
We checked the tissue specificity by western blot, and the result is shown in Figure 3 (33KD, similar to the known MW in uniprot). A promising result could be expected by the researchers through using this specific antibody and high-purity recombinant protein. Abnormal expression of CDK1 is related to the cancer, so rapid and accurate CDK1 measurement is very important for cancer research. In order to facilitate the researchers, the ELISA kit (Catalog No.: PAB888Hu01) for human CDK1 is researched and produced by Cloud-Clone. Corp.. This kit is suitable for researchers to monitor CDK1 level in various of biological samples (tissue, cells, etc.).
So far, it is obvious that the cell cycle regulatory protein is very important. The antibody to phospho-CDK1 is an indispensable tool for researchers since the CDK1 belongs to the protein kinase family. A good tool is incredibly important for research work, and the story of phosphospecific antibody to CDK1 is to be continued in the next topic.
