AMPK Signal Pathway--New Tendency in the Research of Obesity and Type II Diabetes
With the consecutive improvement of life quality, there are more and more obese patients. According to the statistics, at least 2 million and 600 thousand people die of obesity each year. As one of the biggest killer of life, obesity can lead to a variety of metabolic diseases, including hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes and so on, which can seriously affect the health. In order to keep the obese people from disease, scientists pay more attention to research the mechanism and treatment of obesity. The AMPK signaling pathway can regulate the intracellular ATP supply as AMPK is an energy detector for intracellular ATP levels. Considering the central role of AMPK in regulating the metabolism of glucose, lipid, protein and other substances, it is regarded as a key target for the therapy of obesity and type II diabetes.
How does AMPK affect obesity and insulin dependent diabetes? Next, we will show the mechanism how the activation of AMPK regulate the glucose and lipid metabolism in cells and the relationship with obesity and type II diabetes.
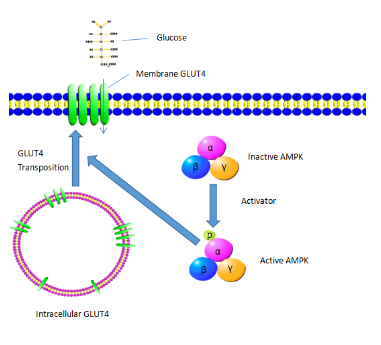
1. Glucose intake
For type II diabetic patients, insulin mediated glucose uptake and utilization were significantly
impaired. It is because of
the decrease in mRNA and protein level of GLUT4 in skeletal muscle cells of diabetic patients. However, the located at skeletal muscle cell membrane can mediate the glucoses into the cell
and be further utilized. When
AMPK is activated, the GLUT4 is induced to transfer to skeletal muscle cell membrane. And then more and more glucoses are transferred into the cell and to be utilized. The hypoglycemic effect of AMPK is not affected by insulin resistance and not mediated by insulin signal transduction pathway, shown in Fig. 1.
2. Oxidation of fatty acids
Excessive accumulation of cholesterol and fatty acids in liver and skeletal muscle can initiate or promote type II diabetes. Activated AMPK can inactivate the main enzymes in cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis (3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase, HMGCR and Acetyl Coenzyme A Carboxylase, ACAC) by phosphorylation. And the synthesis of cholesterol and fatty acid is suppressed. In addition, phosphorylated ACC loses activity and leads to the decline of Malonyl-CoA level to promote the oxidation of fatty acids.
3. Regulation of food intake.
In the hypothalamus, Leptin and Ghrelin both have effect on AMPK to regulate the appetite. Leptin inhibits AMPK activation and cause anorexia to reduce the food intake and weight lose. While the Ghrelin activates AMPK to increase the food intake. That is to say, the AMPK functions on central and peripheral system are opposite.
In conclusion, AMPK and its signaling pathway are the effective pharmacological target for the development of new type II diabetes drugs, as the AMPK have important roles in regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Scientists have developed a series of direct and indirect AMPK agonists, including biguanides (melbine), Phase I/II clinical drug (Acadesine, thienopyridine ketone and pyrrolo pyridine ketone) and the latest one (IP6K1 inhibitor TNP), etc..
The related product for this new tendency are shown below, please focus on it.
| Related Compounds | CCC | Item |
| GLUT4 | C023 | Glucose Transporter 4 (GLUT4) |
| HMGCR | D686 | 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase (HMGCR) |
| ACAC | B284 | Acetyl Coenzyme A Carboxylase Alpha (ACACa) |
| D660 | Acetyl Coenzyme A Carboxylase Beta (ACACb) | |
| Leptin | A084 | Leptin (LEP) |
| Ghrelin | A991 | Ghrelin (GHRL) |
After a brief introduction, if the client want to further investigate the AMPK signaling pathway and perform related experiments, welcome to contact Cloud-Clone Corp. (www.cloud-clone.us).
