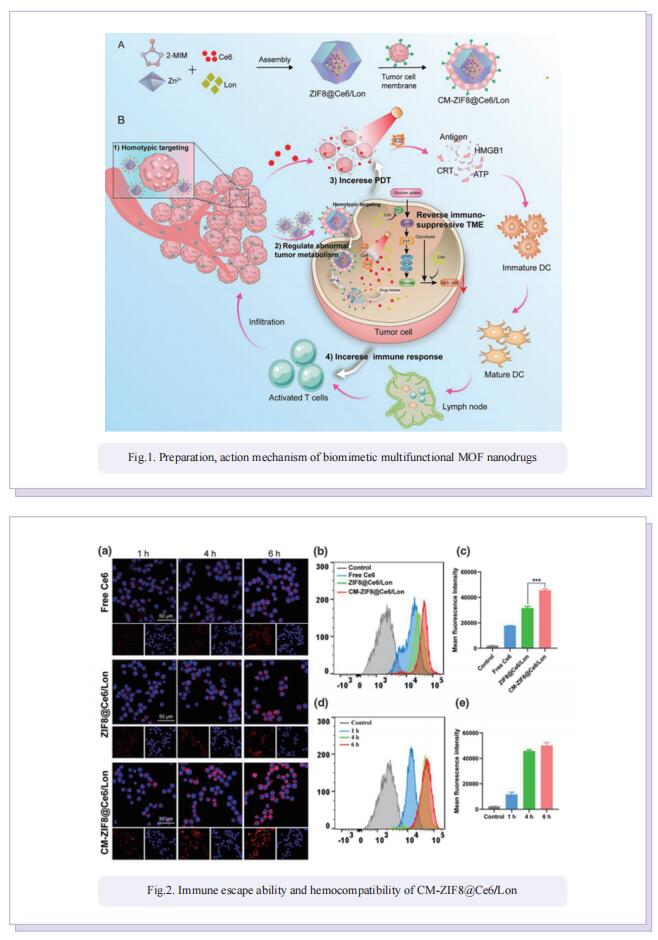
Biomimetic multifunctional nanodrugs enable regulating abnormal tumor metabolism and amplifying PDT-induced immunotherapy for synergistically enhanced tumor ablation

On August 3, 2023, Wei Huang, State Key Laboratory of Bioactive Substance and Function of Natural Medicines, Department of Pharmaceutics, Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, China, and his team published a paper titled “Biomimetic multifunctional nanodrugs enable regulating abnormal tumor metabolism and amplifying PDT-induced immunotherapy for synergistically enhanced tumor ablation” in Materials Today. They reported a biomimetic multifunctional nanoparticle to regulate abnormal tumor metabolism and reverse immunosuppressive microenvironment for boosting anti-tumor immunotherapy.

The kit [ELISA Kit for Interferon Gamma (IFNg), SEA049Mu] of Cloud-Clone brand was chosed in this article, we are so proud for supporting the reaserchers.

Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which does not express the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is a highly aggressive type of breast cancer, accounting for almost 15–20% of all newly diagnosed breast cancers. Patients with TNBC generally have a dismal prognosis due to its high malignancy, easy metastatic risk and high recurrence, in which 5-year survival are less than 10%. Unfortunately, TNBC tumors show poor responses to conventional molecular targeted treatments because lacking any of the targets. Recently, immunotherapy has emerged as a promising strategy for TNBC treatment. Immunotherapy eliminates primary and metastatic tumors by activating the host immune system. However, due to the highly immunosuppressive tumour microenvironment (TME), only a small proportion of patients have durable responses to the current single immunotherapy. Hence, developing efficient strategies that reshape the tumor-immune microenvironment are crucial to improve immunotherapy.
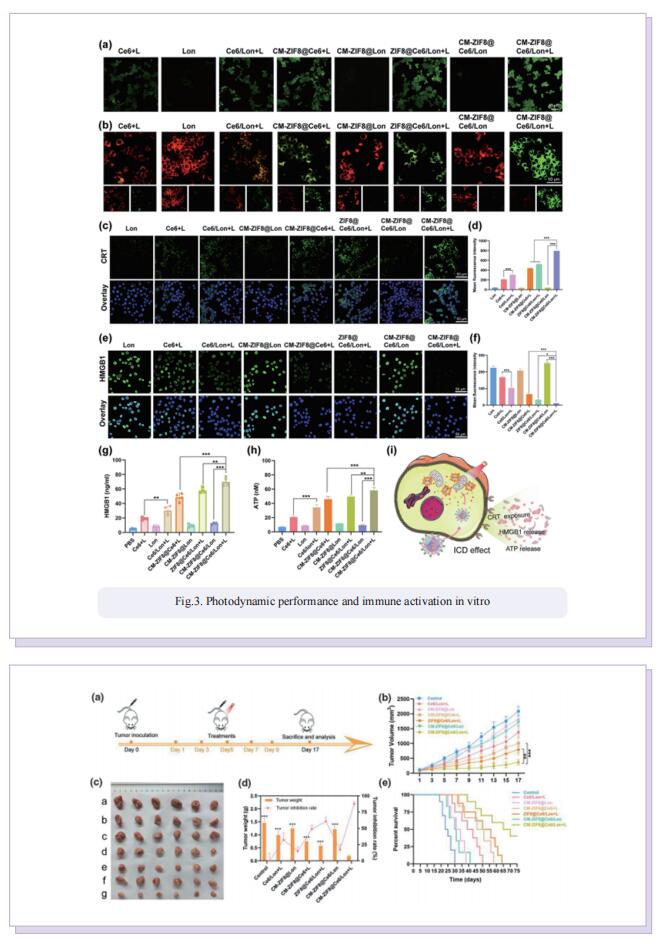
Photodynamic (PDT) induced immunotherapy has attracted remarkable attention. However, PDT aggravate tumor hypoxia, which would further promote cancer metabolism activities and exacerbate immunosuppressive TME. Lonidamine (Lon) is an effective metabolic regulator, which could disrupt the metabolic homeostasis and lead to the reduction of lactate secretion by blockade of hexokinase (HK) signaling. Blockade of HK signaling could inhibit glycolysis activity and decrease the abnormal tumor metabolism. In this study, they developed biomimetic multifunctional nanoparticles to regulate tumor metabolism and amplify PDT-induced immunotherapy for synergistically enhanced TNBC tumor ablation. These multifunctional nanoparticles (CM-ZIF8@Ce6/Lon) were fabricated by homotypic 4T1 tumor cell membrane (CM)-camouflaged zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanoparticles, which coencapsulated with photosensitizer Ce6 and metabolic modulator Lon. Benefiting from the specific homotypic targeting property of 4T1-derived CM, CM-ZIF8@Ce6/Lon could actively accumulate into tumor and enhance cellular uptake. After being internalized into tumor cells, the metabolic modulators Lon inhibited abnormal tumor metabolism and lead to lactate depletion, which reversed the immunosuppressive TME and tumor hypoxia. The regulation of tumor metabolism disorders synergistically enhanced Ce6-triggered PDT efficiency and augmented PDT-mediated immunotherapy against TNBC tumors. As a result, CM-ZIF8@Ce6/Lon efficiently inhibited the primary and metastatic tumor.
In summary, CM-ZIF8@Ce6/Lon could regulate abnormal tumor metabolism and reverse immunosuppressive microenvironment for boosting anti-tumor immunotherapy. The study demonstrated the important potential of regulating abnormal tumor metabolism to boost antitumor immune response, which could provide a new strategy for the design of tumor immunotherapy for the treatment of metastatic TNBC.