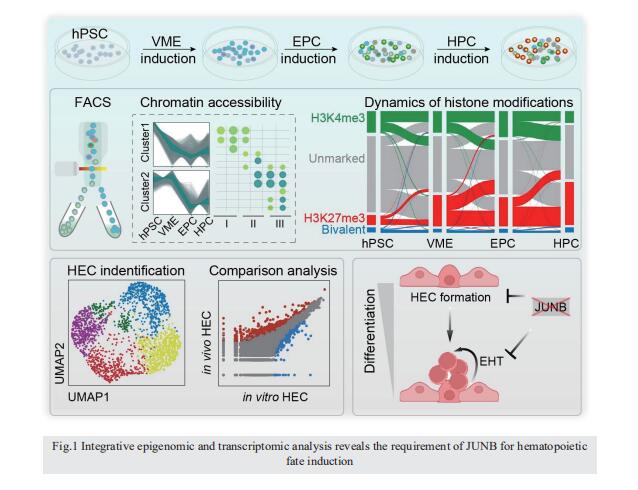
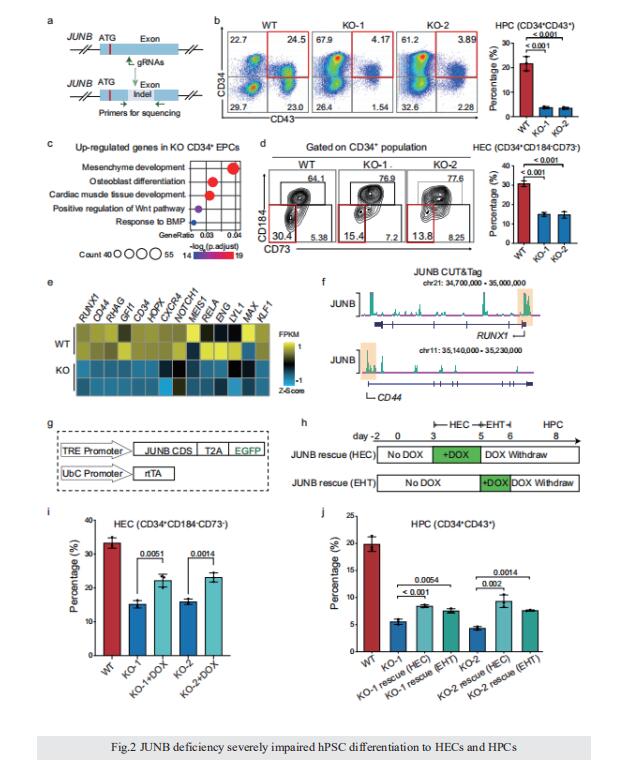
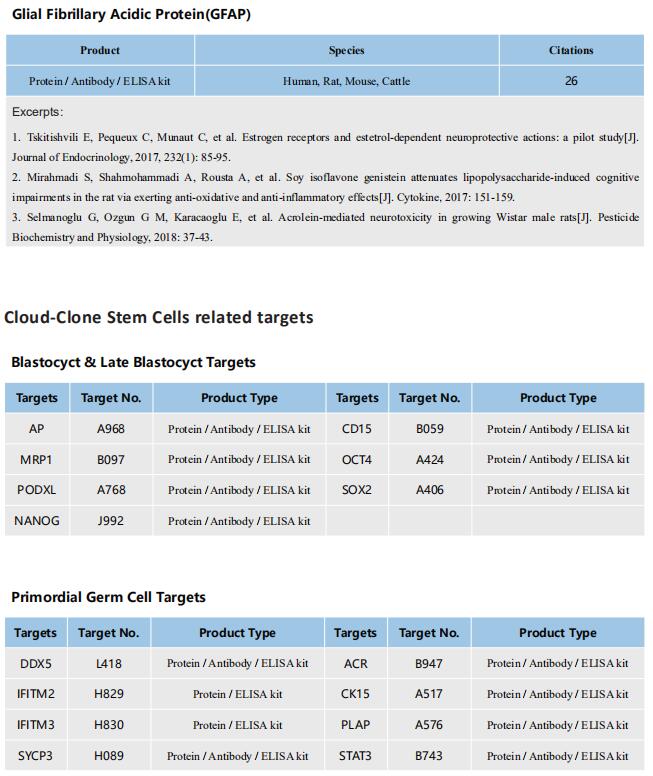
Integrative epigenomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals the requirement of JUNB for hematopoietic fate induction
On 6 June 2022, Jie Na, Center for Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, China, and his team published a paper titled “Integrative epigenomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals the requirement of JUNB for hematopoietic fate induction” in Nature Communications. In this study, they found that JUNB is an essential regulator for hemogenic endothelium specialization and endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition.

The antibodies [None-Linked Guinea pig Anti-Rabbit IgG Polyclonal Antibody, SAA544Rb50] of Cloud-Clone brand was chosed in this article, we are so proud for supporting the reaserchers.
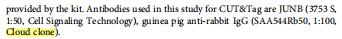

Human pluripotent stem cell differentiation towards hematopoietic progenitor cell can serve as an in vitro model for human embryonic hematopoiesis, but the dynamic change of epigenome and transcriptome remains elusive. Here, we systematically profile the chromatin accessibility, H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 modifications, and the transcriptome of intermediate progenitors during hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation in vitro. The integrative analyses reveal sequential opening-up of regions for the binding of hematopoietic transcription factors and stepwise epigenetic reprogramming of bivalent genes. Single-cell analysis of cells undergoing the endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition and comparison with in vivo hemogenic endothelial cells reveal important features of in vitro and in vivo hematopoiesis. We find that JUNB is an essential regulator for hemogenic endothelium specialization and endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition. These studies depict an epigenomic roadmap from human pluripotent stem cells to hematopoietic progenitor cells, which may pave the way to generate hematopoietic progenitor cells with improved developmental potentials.