The total protein quantitative method: Introduction and Advantages & Disadvantages.
Protein quantification isan indispensable part of the biology experiment, this technique has been widelyused in many fields and industries, including biology, food inspection,clinical examination, diagnosis. It is very common and important to make accurateand reliable quantitative analysis of protein in samples in the actualoperation process. Although so many protein quantitative methods can be usedfor the purpose, there is no a generaland ideal protein quantitive detection method, which is suitable for all kindssituations. It is because of the great variety protein type, diversity instructure, big variance in molecular weight and different functions. Now weintroduce the common protein quantitive detection method, advantages anddrawbacks. The experimental researcher can choose the appropriate quantitativemethod according to the experimental demands.
Protein quantificationmethod can be divided into the following two categories, chemical assay, includingfolin phenol method (Lowry), bicinchoninic acid method (BCA), Kjeldahl methodfor nitrogen (Kjeldahl), biuret method (biuret) and Bradford method (Bradford);optical detection methods, including UV detection and fluorescence detection.The commonly used two methods, including BCA assay and UV detection, areintroduced.
1. Bicinchoninic acid assay(BCA)
Principle:BCA assay is the improvedmethod compared to Lowry method. First, the peptide bonds in protein reduceCu2+ ions from the copper(II) sulfate to Cu+. Next, two molecules ofbicinchoninic acid chelate with one Cu+ ion under alkaline conditions, forminga purple-colored complex that strongly absorbs light at a wavelength of 562 nm.The detection range for BCA assay is about 5-200ug/ml. Principle diagram isshown as follows:
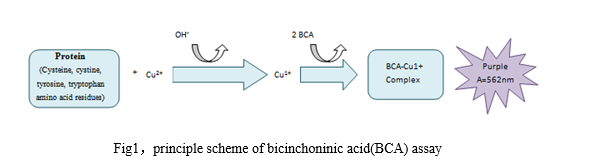
Advantages:Accurate, sensitive(the minimum detection concentration can reach 0.5ug / ml),rapid, simple, economical and practical. Less interfering substances, a goodstability of reagents and the display complex after reaction, high precisionfor the detection of different proteins.
Drawbacks:(1)The detection is easy to be influenced by the following substances:TWEEN,Triton X-100,SDS.(2)Sucrose, urea,ammonium salt, EDTA effect on the determination results。(3)The main drawback isthat different standards will lead to a big gap among the results for the samesample.
2. UV detection
Principle:The conjugated double bond in benzene ring in some amino acid, such as tyrosine,phenylalanine and tryptophan, have ultraviolet absorption peak at 280nm. Forthis, we can measure the total protein concentration by ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy asthe absorbance value is proportional to the content of the conjugated doublebond in benzene ring. The minimum detection concentration can reach 10ug / ml.
Advantages:Simple, sensitive, rapid and no consumption of samples. The sample can berecycled after determination.
Drawbacks:(1)Poor accuracy and specificity of protein determination. (2)Many interferingsubstances, the purine, pyrimidine and nucleic acid in samples can absorbultraviolet material, which may be influence the detection.
For moreinformation,please visit www.cloud-clone.us.
