Regulation of age-associated insulin resistance by MT1-MMP-mediated cleavage of insulin receptor

On June 29, 2022, Zhao-Xiang Bian, School of Chinese Medicine, Hong Kong Baptist University, China, and his team published a paper titled “Regulation of age-associated insulin resistance by MT1-MMP-mediated cleavage of insulin receptor” in Nature Communications. Their findings provided mechanistic insights into regulation of insulin sensitivity during physiological ageing and highlight MT1-MMP as a promising target for therapeutic avenue against diabetes.

The kits [ELISA Kit for Matrix Metalloproteinase 14 (MMP14), SEC056Mu] of Cloud-Clone brand was chosed in this article, we are so proud for supporting the reaserchers.

Insulin sensitivity progressively declines with age. Currently, the mechanism underlying age-associated insulin resistance remains unknown. Here, we identify membrane-bound matrix metalloproteinase 14 (MT1-MMP/MMP14) as a central regulator of insulin sensitivity during ageing. Ageing promotes MMP14 activation in insulin-sensitive tissues, which cleaves Insulin Receptor to suppress insulin signaling. MT1-MMP inhibition restores Insulin Receptor expression, improving insulin sensitivity in aged mice. The cleavage of Insulin Receptor by MT1-MMP also contributes to obesity-induced insulin resistance and inhibition of MT1-MMP activities normalizes metabolic dysfunctions in diabetic mouse models. Conversely, over-expression of MT1-MMP in the liver reduces the level of Insulin Receptor, impairing hepatic insulin sensitivity in young mice. The soluble Insulin Receptor and circulating MT1-MMP are positively correlated in plasma from aged human subjects and non-human primates. Our findings provide mechanistic insights into regulation of insulin sensitivity during physiological ageing and highlight MT1-MMP as a promising target for therapeutic avenue against diabetes.
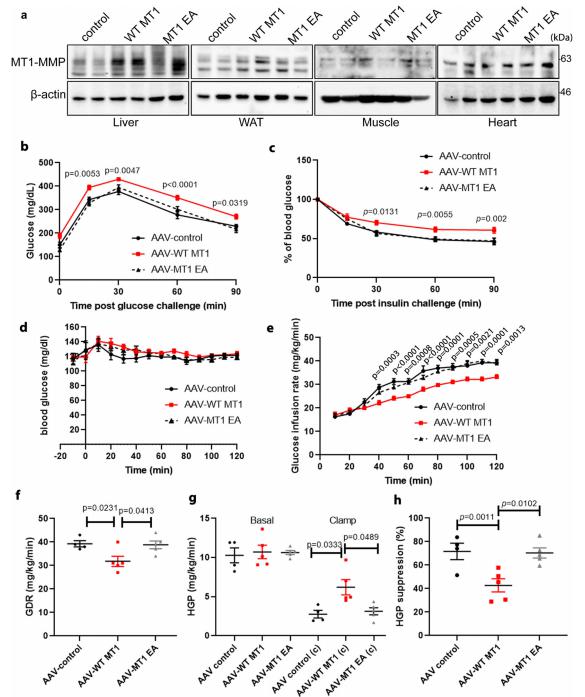
Fig.1 MT1-MMP ectopic expression in the liver induces insulin resistance
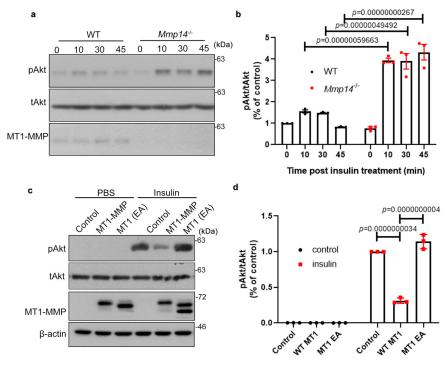
Fig.2 MT1-MMP suppresses insulin signaling in vitro

