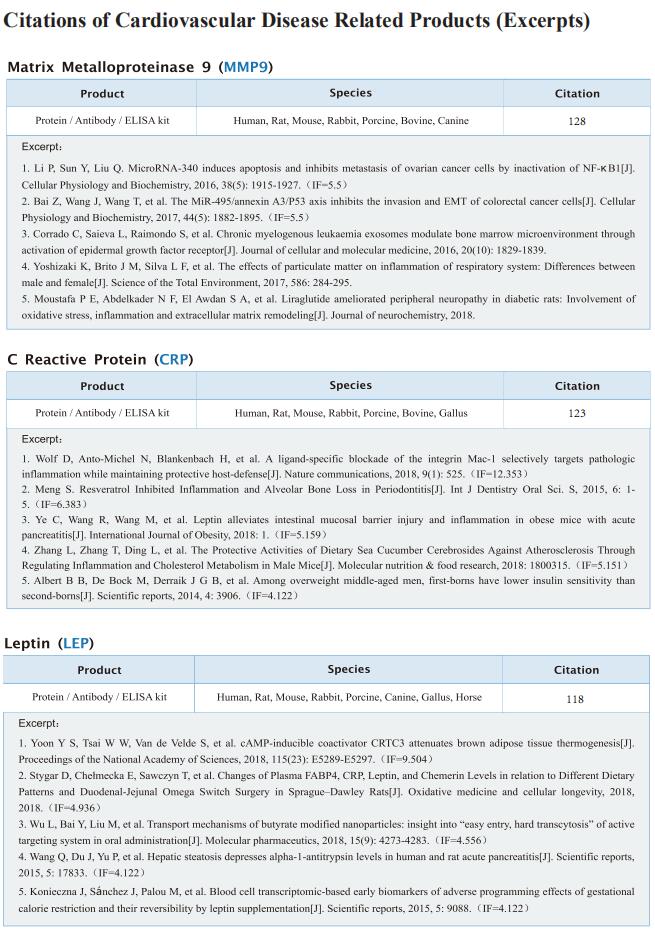
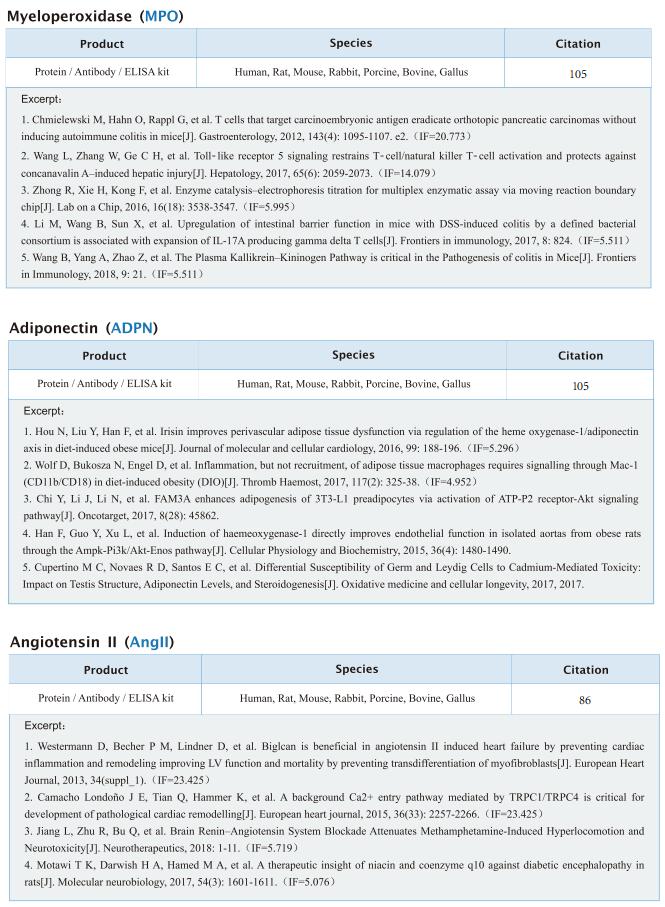
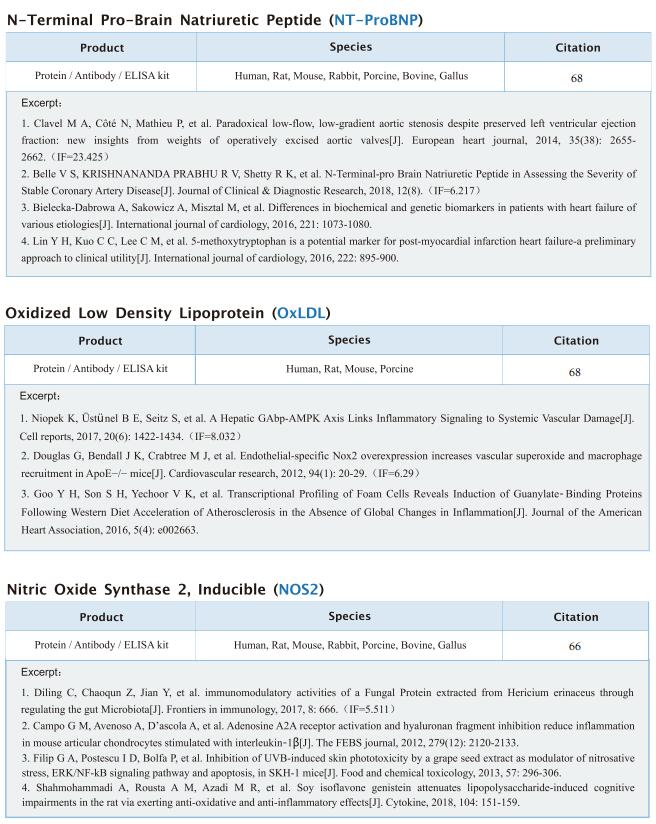
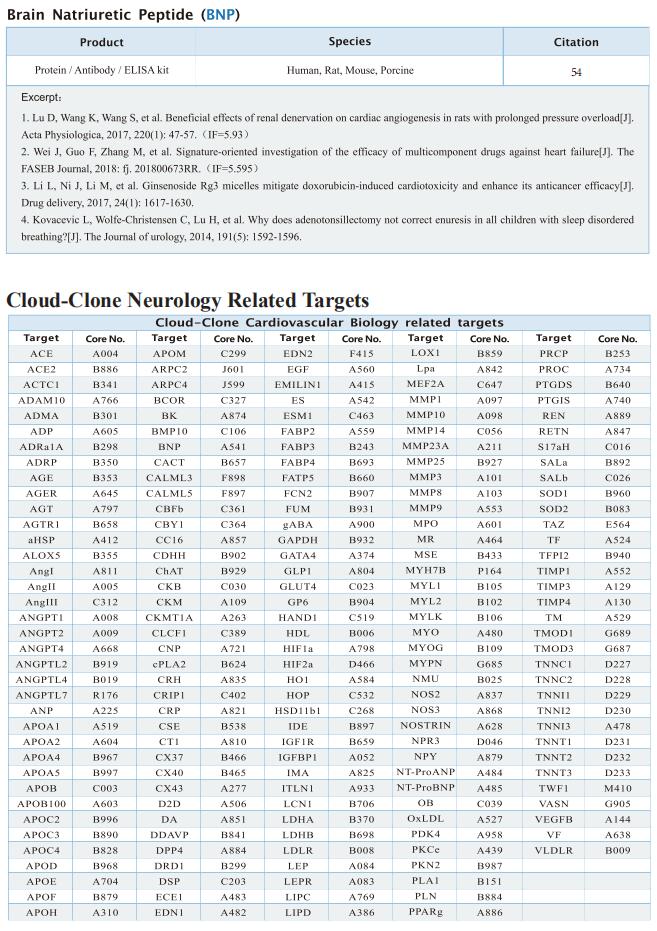
TREM2hi resident macrophages protect the septic heart by maintaining cardiomyocyte homeostasis

On January 12, 2023, Xiangming Fang, Department of Anesthesiology and Intensive Care, The First Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, China, and his team published a paper titled “TREM2hi resident macrophages protect the septic heart by maintaining cardiomyocyte homeostasis” in Nature Metabolism. Their findings suggest that the modulation of TREM2hi cardiac-resident macrophages could serve as a therapeutic strategy for SICM.

The kits [ELISA Kit for Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP), SEA225Mu; ELISA Kit for N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide (NT-ProBNP), SEA485Mu; ELISA Kit for Cardiac Troponin I (cTnI), SEA478Mu] of Cloud-Clone brand was chosed in this article, we are so proud for supporting the reaserchers.

Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy (SICM) is common in septic patients with a high mortality and is characterized by an abnormal immune response. Owing to cellular heterogeneity, understanding the roles of immune cell subsets in SICM has been challenging. Here we identify a unique subpopulation of cardiac-resident macrophages termed CD163+RETNLA+(Mac1), which undergoes self-renewal during sepsis and can be targeted to prevent SICM. By combining single-cell RNA sequencing with fate mapping in a mouse model of sepsis, we demonstrate that the Mac1 subpopulation has distinct transcriptomic signatures enriched in endocytosis and displays high expression of TREM2 (TREM2hi). TREM2hi Mac1 cells actively scavenge cardiomyocyte-ejected dysfunctional mitochondria. Trem2 deficiency in macrophages impairs the self-renewal capability of the Mac1 subpopulation and consequently results in defective elimination of damaged mitochondria, excessive inflammatory response in cardiac tissue, exacerbated cardiac dysfunction and decreased survival. Notably, intrapericardial administration of TREM2hi Mac1 cells prevents SICM. Our findings suggest that the modulation of TREM2hi Mac1 cells could serve as a therapeutic strategy for SICM.
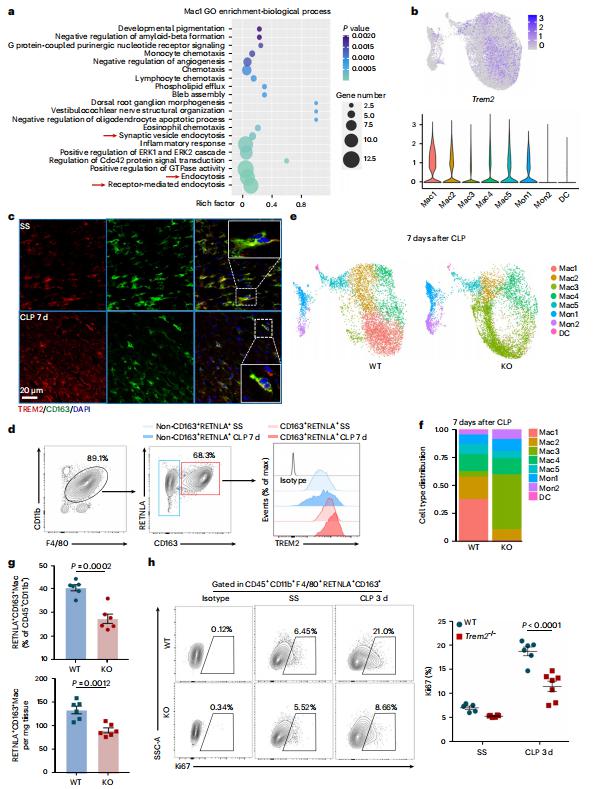
Fig.1 TREM2 is highly expressed on Mac1 subset and essential for Mac1 cells self-renewal in SICM
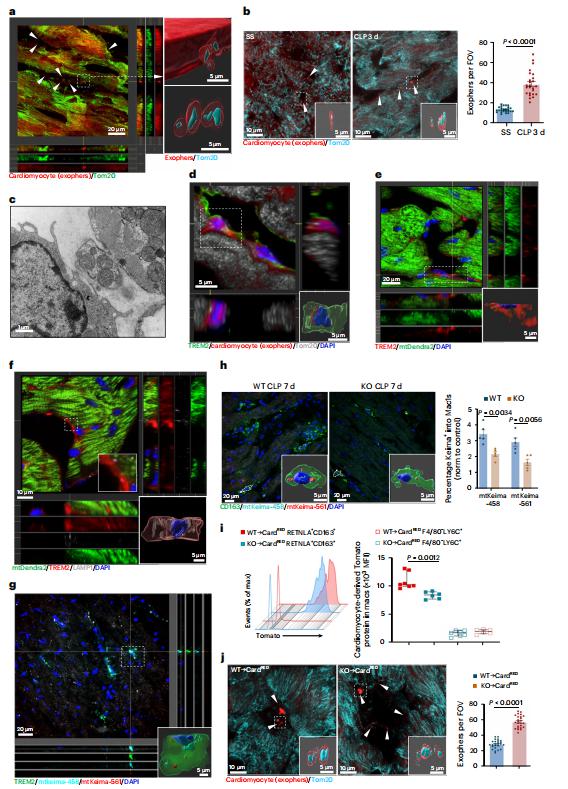
Fig.2 TREM2 promotes the uptake of cardiomyocyte-derived mitochondria by Mac1 in septic heart
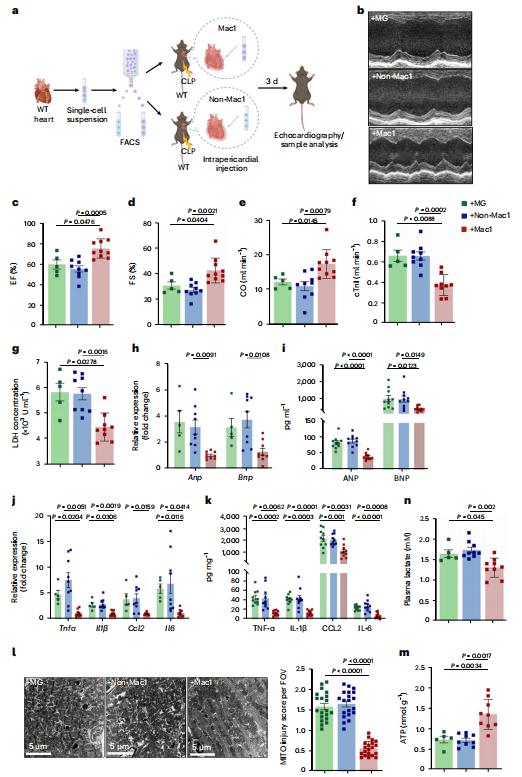
Fig.3 Intrapericardial administration of TREM2hi Mac1 cells protects SICM