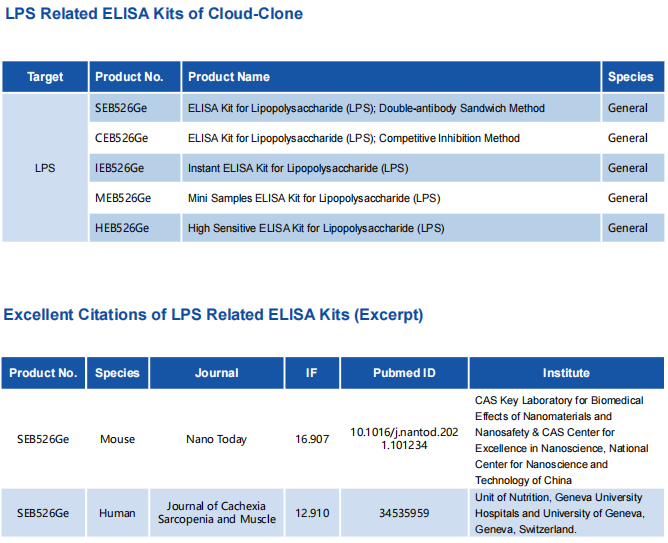
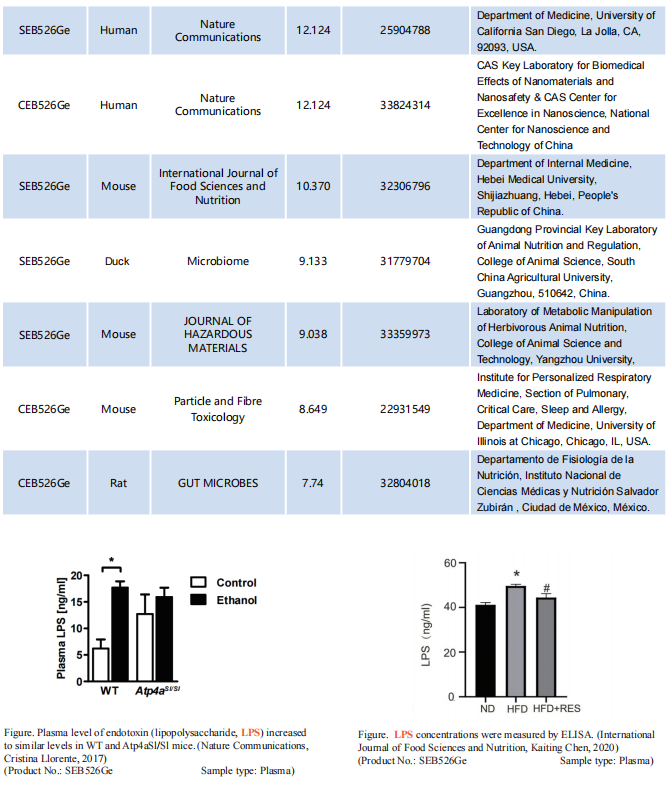
Top-Ranked ELISA Kits (Lipopolysaccharide LPS). Vol.17

Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is the component of the outer wall of gram-negative bacteria cell wall, and it consists of three components: lipid A, core polysaccharide and O-antigen. The lipid A of LPS enters the lipid layer as a component of the outer layer of the lipid bilayer, and the sugar chain is exposed outside the cell, and exists in this form on the cell surface of Gram-negative bacteria. LPS is difficult to come off the cell wall. When bacteria die, it will come off by dissolving and destroying cells, and exert its toxicity by acting on animal cells. Because of this nature, it is not a toxin secreted by bacteria outside the body (exotoxin), but a toxin that does not secrete, so it is also called endotoxin. LPS can activate monocyte macrophages, endothelial cells and epithelial cells through cell signal transduction system in the body, synthesize and release a variety of cytokines and inflammatory mediators, and then cause a series of reactions in the body.