Translational Selenium Nanoparticles to Attenuate Allergic Dermatitis through Nrf2- Keap1-Driven Activation of Selenoproteins

On July 10, 2023, Tianfeng Chen, Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Department of Chemistry, China, and his team published a paper titled “Translational Selenium Nanoparticles to Attenuate Allergic Dermatitis through Nrf2- Keap1-Driven Activation of Selenoproteins” in ACS Nano. This study not only constructs facile large-scale synthesis of translational Se nanomedicine to break through the bottleneck problem of nanomaterials but also sheds light on its application in the intervention and treatment of allergies.

The kit [ELISA Kit for Histamine (HA), CEA927Ge] of Cloud-Clone brand was chosed in this article, we are so proud for supporting the reaserchers.

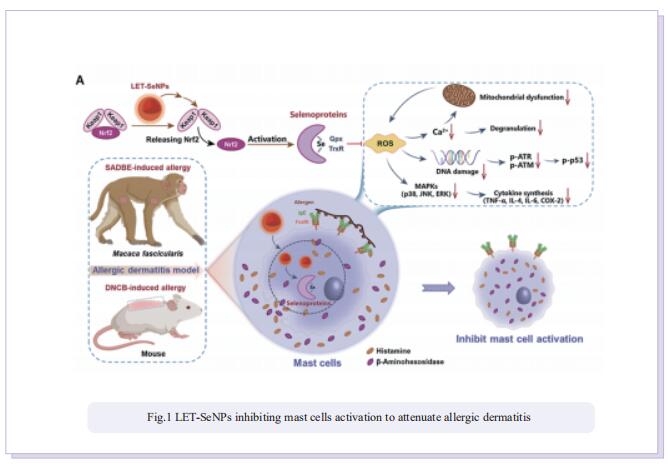
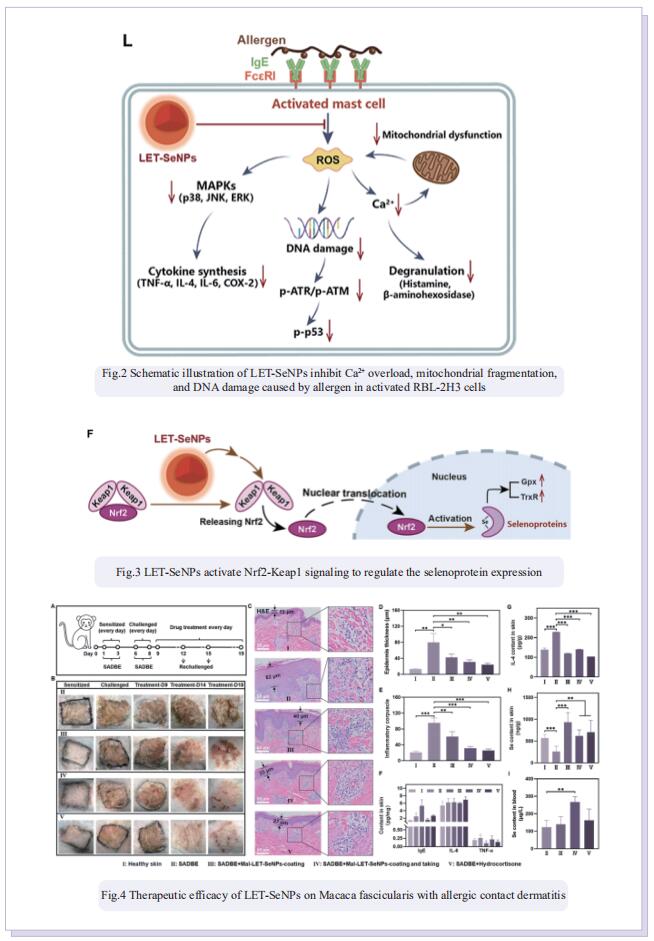
Easy recurrence and strong treatment side effects significantly limit the clinical treatment of allergic dermatitis. The human trace element selenium (Se) plays essential roles in redox regulation through incorporation into selenoproteins in the form of 21st necessary amino acid selenocysteine, to participates in the pathogenesis and intervention of chronic inflammatory diseases. Therefore, based on the safe and elemental properties of Se, we construct a facile-synthesis strategy for antiallergic selenium nanoparticles (LET-SeNPs), and scale up the production by employing a spray drying method with lactose (Lac-LET-SeNPs) or maltodextrin (Mal-LET-SeNPs) as encapsulation agents realizing larger scale production and a longer storage time. As expected, these as-prepared LET-SeNPs could effectively activate the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway to enhance the expression of antioxidative selenoprotein at mRNA and protein levels, then inhibit mast cell activation to achieve efficient antiallergic activity. Interestingly, LET-SeNPs undergo metabolism to seleno-amino acids to promote biosynthesis of selenoproteins, which could suppress ROS-induced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and MAPKs activation to suppress the release of histamine and inflammatory cytokines. Allergic mouse and Macaca fascicularis models further confirm that LET-SeNPs could increase the Se content and selenoprotein expression in the skin, decrease mast cells activation and inflammatory cells infiltration, and finally exhibit the high therapeutic effects on allergic dermatitis. Taken together, this study not only constructs facile large-scale synthesis of translational Se nanomedicine to break through the bottleneck problem of nanomaterials but also sheds light on its application in the intervention and treatment of allergies.