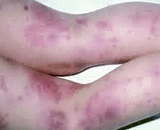
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis.[3] Vasculitis is primarily caused by leukocyte migration and resultant damage. Laboratory tests of blood or body fluids are performed for patients with active vasculitis. Their results will generally show signs of inflammation in the body, such as increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), elevated C-reactive protein (CRP), anemia, increased white blood cell count and eosinophilia. Other possible findings are elevated antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) levels and hematuria.