Active Apolipoprotein C1 (APOC1)
Apo-C1; Truncated apolipoprotein C-I
- Product No.APA252Hu02
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- Buffer FormulationPBS, pH7.4, containing 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder
- Purity> 90%
- Isoelectric Point9.1
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 10µg50µg 200µg 1mg 5mg
- FOB
US$ 236
US$ 590
US$ 1180
US$ 3540
US$ 8850
For more details, please contact local distributors!
ACTIVITY TEST
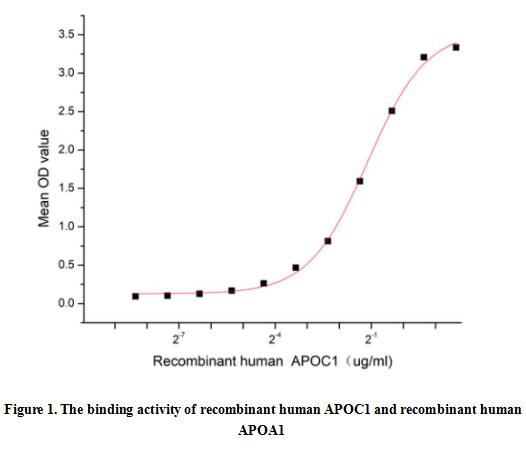
Apolipoprotein C1 (APOC1), also known as Apo-CI; ApoC-I; apo-CIB; apoC-IB, is the smallest size apolipoprotein of all apolipoprotein C family (Mr = 6.6 kDa) and located at position 19q13.32. APOC1 is primarily expressed in the liver and activated when monocytes differentiate into macrophages. It plays important roles in the innate immune response as effector of glucocorticoid-mediated responses and regulator of the inflammatory process. It has anti-inflammatory activity and also can promote the differentiation of T-cells into Th1 cells and negatively regulates differentiation into Th2 cells. Besides, Apolipoprotein A1 (APOA1) has been identified as an interactor of APOC1, thus a functional binding ELISA assay was conducted to detect the interaction of recombinant human APOC1 and recombinant human APOA1. Briefly, APOC1 was diluted serially in PBS with 0.01% BSA (pH 7.4). Duplicate samples of 100 μl were then transferred to APOA1-coated microtiter wells and incubated for 1h at 37℃. Wells were washed with PBST and incubated for 1h with anti-APOC1 pAb, then aspirated and washed 3 times. After incubation with HRP labelled secondary antibody for 1h at 37℃, wells were aspirated and washed 5 times. With the addition of substrate solution, wells were incubated 15-25 minutes at 37℃. Finally, add 50 µL stop solution to the wells and read at 450/630 nm immediately. The binding activity of recombinant human APOC1 and recombinant human APOA1 was shown in Figure 1, the EC50 for this effect is 0.46 ug/mL.
USAGE
Reconstitute in 10mM PBS (pH7.4) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
STORAGE
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
STABILITY
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
| Magazine | Citations |
| PROTEOMICS - Clinical Applications | Proteomic and genomic analyses suggest the association of Apolipoprotein C1 with abdominal aortic aneurysm Onlinelibrary: prca.201300119 |
| Journal of Dairy Science | Colostrum and milk protein rankings and ratios of importance to neonatal calf health using a proteomics approach pubmed:28189329 |
| RESPIRATORY RESEARCH | The HDL from septic-ARDS patients with composition changes exacerbates pulmonary endothelial dysfunction and acute lung injury induced by cecal ligation … Pubmed: 33148285 |







