Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
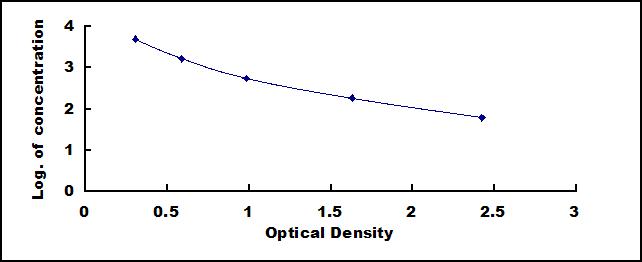
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


ELISA Kit for Carboxymethyl Lysine (CML)
N(6)-Carboxymethyllysine
- Product No.CEB977Ge
- Organism SpeciesPan-species (General) Same name, Different species.
- Sample TypeSerum, plasma and other biological fluids
- Test MethodCompetitive Inhibition
- Assay Length2h
- Detection Range61.7-5,000ng/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 25.9ng/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 48T96T 96T*5 96T*10 96T*100
- FOB
US$ 565
US$ 808
US$ 3634
US$ 6864
US$ 56525
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Carboxymethyl Lysine (CML).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Carboxymethyl Lysine (CML) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of Carboxymethyl Lysine (CML) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Carboxymethyl Lysine (CML) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 79-98 | 90 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 82-93 | 87 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 82-104 | 89 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Carboxymethyl Lysine (CML) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Carboxymethyl Lysine (CML) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Carboxymethyl Lysine (CML) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 83-101% | 98-105% | 87-95% | 87-94% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 82-102% | 99-105% | 80-95% | 87-101% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 91-105% | 91-103% | 91-98% | 89-103% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 50µL standard or sample to each well.
And then add 50µL prepared Detection Reagent A immediately.
Shake and mix. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
4. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
5. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
6. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
7. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450 nm immediately.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
| Magazine | Citations |
| PLoS ONE | Advanced Glycation End Products Induce Human Corneal Epithelial Cells Apoptosis through Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species and Activation of JNK and p38 MAPK Pathways PubMed: PMC3680386 |
| Int J Vitam Nutr Res. | Effects of combined lipoic acid and pyridoxine on albuminuria, advanced glycation end-products, and blood pressure in diabetic nephropathy. Pubmed: 24491880 |
| Geriatr Gerontol Int | Advanced glycation end-products accelerate the cardiac aging process through the receptor for advanced glycation end-products/transforming growth factor-β-Smad signaling pathway in cardiac fibroblasts PubMed: 26016731 |
| J Agric Food Chem | Inhibition of Advanced Glycation Endproduct Formation by Lotus Seedpod Oligomeric Procyanidins through RAGE-MAPK Signaling and NF-κB Activation in High-Fat-Diet Rats. PubMed: 26207852 |
| Journal of Diabetes and Its Complications. | Association of serum N Îľ-Carboxy methyl lysine with severity of diabetic retinopathy Pubmed:26782022 |
| J Nat Med. | Hyperoside reduces albuminuria in diabetic nephropathy at the early stage through ameliorating renal damage and podocyte injury. Pubmed:27255369 |
| J Diabetes Complications | Increased levels of N(ε)- Carboxy methyl lysine (N(ε)-CML) are associated with topographic alterations in retinal pigment epithelium: A preliminary study Pubmed:27039312 |
| J Nutr Biochem. | Long-term administration of advanced glycation end-product stimulates the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and sparking the development of renal injury. pubmed:27816762 |
| Renal Failure | Plasma heparanase is associated with blood glucose levels but not urinary microalbumin excretion in type 2 diabetic nephropathy at the early stage pubmed:28994624 |
| Nutrition, Metabolism, and Cardiovascular Diseases | High intake of dietary advanced glycation end-products is associated with increased arterial stiffness and inflammation in subjects with type 2 diabetes. pubmed:28958695 |
| Journal of Food Science and Technology | Antiglycation and antioxidant activities of mogroside extract from (Swingle) fruits Pubmed:29666541 |
| Indian J Ophthalmol | Elevated advanced glycation end products are associated with subfoveal ellipsoid zone disruption in diabetic macular edema 34708772 |
| Catalog No. | Related products for research use of Pan-species (General) Organism species | Applications (RESEARCH USE ONLY!) |
| CEB977Ge | ELISA Kit for Carboxymethyl Lysine (CML) | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection. |
| LMB977Ge | Multiplex Assay Kit for Carboxymethyl Lysine (CML) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) | FLIA Kit for Antigen Detection. |