Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
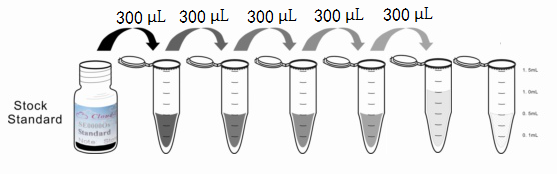
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


Multiplex Assay Kit for Epithelial Neutrophil Activating Peptide 78 (ENA78) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay)
CXCL5; SCYB5; Chemokine C-X-C-Motif Ligand 5; Small Inducible Cytokine Subfamily B(Cys-X-Cys),Member 5; Neutrophil-activating peptide ENA-78
(Note: Up to 8-plex in one testing reaction)
- Product No.LMA860Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- Sample Typeserum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3.5h
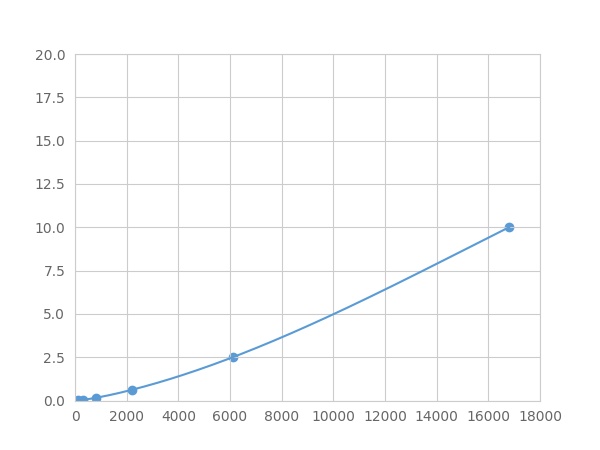
- Detection Range0.01-10ng/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 0.003 ng/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 8Plex 7Plex 6Plex 5Plex 4Plex 3Plex 2Plex1Plex
- FOB
US$ 348
US$ 362
US$ 382
US$ 409
US$ 436
US$ 476
US$ 536
US$ 670
Add to Price Calculator
Result
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Epithelial Neutrophil Activating Peptide 78 (ENA78) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Epithelial Neutrophil Activating Peptide 78 (ENA78) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Epithelial Neutrophil Activating Peptide 78 (ENA78) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Epithelial Neutrophil Activating Peptide 78 (ENA78) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 80-92 | 88 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 80-88 | 84 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 80-99 | 85 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Epithelial Neutrophil Activating Peptide 78 (ENA78) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Epithelial Neutrophil Activating Peptide 78 (ENA78) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Epithelial Neutrophil Activating Peptide 78 (ENA78) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 78-90% | 90-102% | 92-99% | 78-91% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 91-99% | 93-101% | 92-105% | 97-105% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 91-101% | 91-98% | 85-93% | 96-105% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| 96-well plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Pre-Mixed Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Magnetic beads (22#:ENA78) | 1 | Analysis buffer | 1×20mL |
| Pre-Mixed Detection Reagent A | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B (PE-SA) | 1×120μL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| Sheath Fluid | 1×10mL | Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL |
| Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Preparation of standards, reagents and samples before the experiment;
2. Add 100μL standard or sample to each well,
add 10μL magnetic beads, and incubate 90min at 37°C on shaker;
3. Remove liquid on magnetic frame, add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 60min at 37°C on shaker;
4. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
5. Add 100μL prepared Detection Reagent B, and incubate 30 min at 37°C on shaker;
6. Wash plate on magnetic frame for three times;
7. Add 100μL sheath solution, swirl for 2 minutes, read on the machine.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
| Magazine | Citations |
| Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology | Ameliorative Effects of Curcumin on Fibrinogen-Like Protein-2 Gene Expression, Some Oxido-Inflammatory and Apoptotic Markers in a Rat Model of l-Arginine-Induced Acute Pancreatitis. Pubmed:26862043 |
| Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology | Ameliorative Effects of Curcumin on Fibrinogen-Like Protein-2 Gene Expression, Some Oxido-Inflammatory and Apoptotic Markers in a Rat Model of l-Arginine-Induced Acute Pancreatitis pubmed:26862043 |
| OncoTargets and Therapy | The clinical significance of CXCL5 in non-small cell lung cancer. pubmed:29200871 |
| Biochimie | Activated CXCL5-CXCR2 axis promotes the migration, invasion and EMT of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells via modulation of β-catenin pathway Pubmed:29471001 |
| Cancer Biology & Therapy | Activation of CXCL5-CXCR2 axis promotes proliferation and accelerates G1 to S phase transition of papillary thyroid carcinoma cells and activates JNK and p38 … Pubmed: 30404567 |
| Respiratory Research | Phospholipase Cε plays a crucial role in neutrophilic inflammation accompanying acute lung injury through augmentation of CXC chemokine production from … Pubmed: 30634975 |
| American Journal of Pathology | Interleukin17–CXCR2 axis facilitates breast cancer progression by up-regulating neutrophil recruitment Pubmed: 31654638 |
| Bioactive Materials | Secretions from hypochlorous acid-treated tumor cells delivered in a melittin hydrogel potentiate cancer immunotherapy 34820587 |
| Am J Cancer Res | Differential expression profile of CXC-receptor-2 ligands as potential biomarkers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Pubmed:35141005 |