Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


Mini Samples ELISA Kit for Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23)
ADHR; HYPF; HPDR2; PHPTC; Phosphatonin; Tumor-derived hypophosphatemia-inducing factor
- Product No.MEA746Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- Sample Typeserum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3h
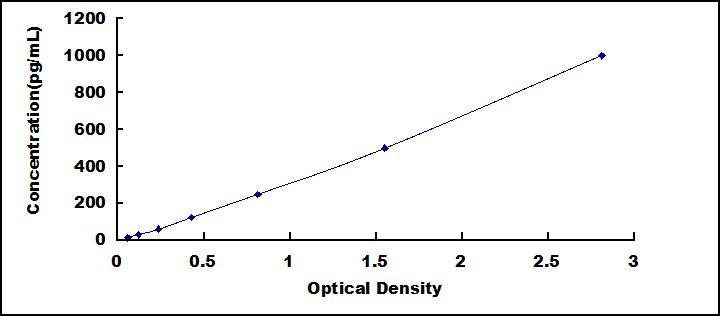
- Detection Range15.6-1,000pg/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 6.2pg/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 48T96T 96T*5 96T*10 96T*100
- FOB
US$ 529
US$ 756
US$ 3402
US$ 6426
US$ 52920
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Mini Samples Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Mini Samples Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Mini Samples Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Mini Samples Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 84-104 | 95 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 88-95 | 91 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 82-98 | 89 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Mini Samples Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Mini Samples Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Mini Samples Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 80-97% | 78-93% | 84-102% | 83-97% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 89-96% | 95-104% | 94-101% | 85-98% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 84-101% | 80-92% | 89-96% | 78-101% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×60µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×6mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×60µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×6mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×4.5mL | Stop Solution | 1×3mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×10mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 25µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 25µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 25µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 25µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 20µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
| Magazine | Citations |
| Journal of international medicine | Prognostic impact of renal function in precapillary pulmonary hypertension Pubmed: 24011362 |
| BMC Nephrology | FGF-23 associated with the progression of coronary artery calcification in hemodialysis patients Pubmed: 24180481 |
| Journal of Clinical Densitometry | Lower Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 Levels in Young Adults With Crohn Disease as a Possible Secondary Compensatory Effect on the Disturbance of Bone and Mineral Metabolism Pubmed: 23623649 |
| J Intern Med. | Prognostic impact of renal function in precapillary pulmonary hypertension. Pubmed:24011362 |
| Journal of Bone and Mineral Research | Adverse effects of osteocytic constitutive activation of ?-catenin on bone strength and bone growth Pubmed:25639729 |
| Nefrologia | Fibroblast growth factor is associated to left ventricular mass index, anemia and low values of transferrin saturation El factor de crecimiento fibroblástico está asociado con el índice de masa ventricular izquierda, anemia y niveles bajos de saturación de la transferrina PubMed: 26394828 |
| Medicine (Baltimore) | An Attempt to Evaluate Selected Aspects of “Bone–Fat Axis” Function in Healthy Individuals and Patients With Pancreatic Cancer PubMed: 26266370 |
| Ann Biol Clin (Paris) | Les biomarqueurs des calcifications vasculaires: quelles limites analytiques pour leur transfert de la recherche bioclinique à la pratique? PubMed: 26069069 |
| Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology | High-dose fast infusion of parenteral iron isomaltoside is efficacious in inflammatory bowel disease patients with iron-deficiency anaemia without profound changes in phosphate or fibroblast growth factor 23 Pubmed:27326766 |
| PLOS ONE | Prostaglandin-E2 Mediated Increase in Calcium and Phosphate Excretion in a Mouse Model ofDistal Nephron Salt Wasting. pubmed:27442254 |
| Journal of Laboratory Diagnostics | Evaluation of concentration fibroblast growth factor FGF-23 in hemodialysed patients and after kidney transplantation publication:312592751 |
| Journal of Integrative Nephrology & Andrology | Associations between serum fibroblast growth factor 23 level and intradialytic hypotension in hemodialysis patients issn:2394-2916 |
| Journal of Renal Nutrition | ADAM17, a New Player in the Pathogenesis of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder. pubmed:29056164 |
| Experimental Biology and Medicine(Maywood) | Effect of cross-linked chitosan iron (III) on vascular calcification in uremic rats Pubmed:29763365 |
| Psychiatry Research | Cerebrospinal fluid FGF23 levels correlate with a measure of impulsivity Pubmed:29677623 |
| BMC Pediatrics | Serum and urine FGF23 and IGFBP-7 for the prediction of acute kidney injury in critically ill children Pubmed:29907141 |
| Medical Science Monitor | Effect of Salt Intervention on Serum Levels of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) in Chinese Adults: An Intervention Study Pubmed:29608553 |
| International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | Disconnection of pulmonary and systemic arterial stiffness in COPD Pubmed:29881265 |
| Saudi journal of kidney diseases and transplantation | Prevalence of cardiac arrhythmia and risk factors in chronic kidney disease patients Pubmed:29970732 |
| Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation | High-serum phosphate and parathyroid hormone distinctly regulate bone loss and vascular calcification in experimental chronic kidney disease Pubmed: 30189026 |
| BioFactors | Alteration in serum concentrations of FGF19, FGF21, and FGF23 in patients with urothelial carcinoma Pubmed: 30334297 |
| Biological Trace Element Research | Altered Mineral Metabolism and Disequilibrium Between Calcification Promoters and Inhibitors in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients Pubmed: 30847765 |
| Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. | Evaluation of FGF‐23 and 25(OH)D3 levels in peri‐implant sulcus fluid in peri‐implant health and diseases Pubmed: 31407857 |
| JACC-Cardiovascular Imaging | PREVALANCE AND PROGRESSION OF CARDIOVASCULAR CALCIFICATIONS IN HAEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS Pubmed: 28797410 |
| Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl | Serum fibroblast growth factor 23 levels do not correlate with carotid intima-media thickness in patients with chronic kidney disease Pubmed: 31696838 |
| Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy | MiRNA-192-5p attenuates airway remodeling and autophagy in asthma by targeting MMP-16 and ATG7 Pubmed: 31918268 |
| Is Serum FGF-23 Associated with Subclinic Atherosclerosis in Patients with AA Amyloidosis? | |
| THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTERIAL STIFNESS AND 25-(OH) VITAMIN D, FGF 23 IN MAINTENANCE HEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS | |
| THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTERIAL STIFFNESS AND 25-(OH) VITAMIN D, FGF 23 IN MAINTENANCE HEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS KRON?K ¡ | |
| Calcif Tissue Int | The Measurement and Interpretation of Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF23) Concentrations Pubmed:35665817 |
| European Journal of Medical Genetics | Genetic and clinical profile of patients with hypophosphatemic rickets Pubmed:35738466 |
| African Health Sciences | Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF 23) and intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) as markers of mineral bone disease among Nigerians with non-diabetic kidney disease |