Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


ELISA Kit for Fibronectin (FN)
FN1; CIG; FINC; LETS; MSF; GFND2; Anastellin; Migration-Stimulating Factor; Cold-Insoluble Globulin; Large, External, Transformation-Sensitive Protein
- Product No.SEA037Eq
- Organism SpeciesEquus caballus; Equine (Horse) Same name, Different species.
- Sample TypeSerum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, cell culture supernates and other biological fluids
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3h
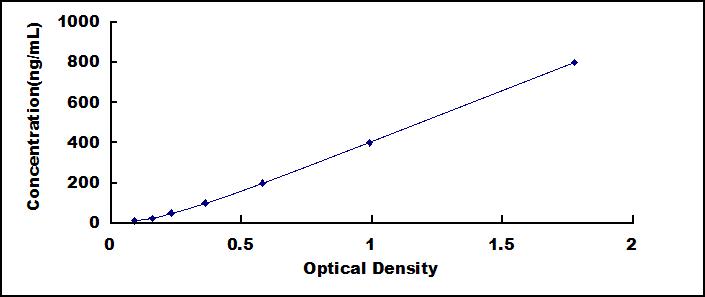
- Detection Range12.5-800ng/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 5.5ng/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 48T96T 96T*5 96T*10 96T*100
- FOB
US$ 542
US$ 774
US$ 3483
US$ 6579
US$ 54180
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Fibronectin (FN).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Fibronectin (FN) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Fibronectin (FN) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Fibronectin (FN) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 80-104 | 90 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 94-102 | 99 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 78-101 | 83 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Fibronectin (FN) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Fibronectin (FN) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Fibronectin (FN) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 98-105% | 86-94% | 78-90% | 95-103% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 82-101% | 94-102% | 87-94% | 90-101% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 80-90% | 88-96% | 79-101% | 88-99% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
-
 Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
-
 Quality Control of Kit
Quality Control of Kit
-
 ELISA Kit Customized Service
ELISA Kit Customized Service
-
 Disease Model Customized Service
Disease Model Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 TGFB1 Activation Reagent
TGFB1 Activation Reagent
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Streptavidin
Streptavidin
-
 Fast blue Protein Stain solution
Fast blue Protein Stain solution -
 Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
-
 Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
| Magazine | Citations |
| American Journal of Physiology - Renal Physiology | Advanced oxidation protein products induce mesangial cell perturbation through PKC-dependent activation of NADPH oxidase PubMed: 19019916 |
| Stem Cell Research Therapy | Protein synthesis and secretion in human mesenchymal cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue and Wharton's jelly Pubmed: 24739658 |
| Molecules. | Identification of compounds from the water soluble extract of Cinnamomum cassia barks and their inhibitory effects against high-glucose-induced mesangial cells. Pubmed: 24013407 |
| Journal of Ethnopharmacology | Bioactive compounds from Cornus officinalis fruits and their effects on diabetic nephropathy ScienceDirect: S0378874114002414 |
| Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science | Inhibition by Female Sex Hormones of Collagen Gel Contraction Mediated by Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells Pubmed: 24609629 |
| PLoS One. | Mesenchymal stromal cell proliferation, gene expression and protein production in human platelet-rich plasma-supplemented media Pubmed:Pmc4130592 |
| Connective Tissue Research | Metabolic and cytoprotective effects of in vivo peri-patellar hyaluronic acid injections in cultured tenocytes Pubmed:25333747 |
| Laryngoscope. | Establishing principles of macromolecular crowding for in vitro fibrosis research of the vocal fold lamina propria Pubmed:25545625 |
| Biomedical Materials | In vivo bioengineered ovarian tumors based on collagen, matrigel, alginate and agarose hydrogels: a comparative study Pubmed:25634132 |
| Biomedical Materials | In vivo PubMed: 25634132 |
| American Journal of Medical and Biological Research | Impact of Nigella Sativa, Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Chromium Picolinate onNF-κB/leptin-insulin Axisin Obese Subjects with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ajmbr: 3 |
| Food Chem. | Comparative proteomics of milk fat globule membrane in goat colostrum and mature milk Pubmed:27173528 |
| journal of perinatal medicine | Maternal endothelial damage as a disorder shared by early preeclampsia, late preeclampsia and intrauterine growth restriction. pubmed:27865093 |
| Chinese Journal of Contemporary Neurology and Neurosurgery | Effect of panax notoginseng saponins on efficacy and hemorrhagic transformation of rt-PA intravenous thrombolysis in patients with acute ischemic stroke Article_en:CJFDTotal-XDJB201611014 |
| Scientific Reports | Serum fbronectin distinguishes the early stages of hepatocellular carcinoma pubmed:28842594 |
| Molecular Medicine Reports | Pigment epithelium‑derived factor protects human glomerular mesangial cells from diabetes via NOXO1‑iNOS suppression 10.3892/mmr.2017.7563 |
| Cell Death & Disease | Tenomodulin is essential for prevention of adipocyte accumulation and fibrovascular scar formation during early tendon healing. pubmed:29022912 |
| Journal of Cellular Biochemistry | Effects of panax notoginseng saponin on the pathological ultrastructure and serum IL‐6 and IL‐8 in pulmonary fibrosis in rabbits Pubmed:29932250 |
| Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy | Corn silk (Zea mays L.), a source of natural antioxidants with α-amylase, α-glucosidase, advanced glycation and diabetic nephropathy inhibitory activities Pubmed: 30530231 |
| Advanced Healthcare Materials | Impact of Hydrogel Elasticity and Adherence on Osteosarcoma Cells and Osteoblasts Pubmed: 30838809 |
| Inflammation | TNF-α Regulates ITGβ1 and SYND4 Expression in Nucleus Pulposus Cells: Activation of FAK/PI3K Signaling Pubmed: 31111299 |
| EBioMedicine | Three kinds of corneal host cells contribute differently to corneal neovascularization |
| Renal Failure | Effects of autophagy on macrophage adhesion and migration in diabetic nephropathy Pubmed: 31352855 |
| Journal of Biological Chemistry | Growth hormone induces Notch1 signaling in podocytes and contributes to proteinuria in diabetic nephropathy Pubmed: 31511328 |
| Neurotherapeutics | Fabrication and Evaluation of a Xenogeneic Decellularized Nerve-Derived Material: Preclinical Studies of a New Strategy for Nerve Repair Pubmed: 31758411 |
| FASEB Journal | Molecular hydrogen regulates PTEN‐AKT‐mTOR signaling via ROS to alleviate peritoneal dialysis‐related peritoneal fibrosis Pubmed: 31930571 |
| Journal of Clinical Medicine | Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns and Th-Cell-Related Cytokines Released after Progressive Effort Pubmed: 32210109 |
| International Journal of Women¡¯s Health and Reproduction Sciences | Are the Circulating Levels of Copeptin and Fibronectin Dysregulated in Preeclamptic South African Black Women? |
| Advanced glycation end-products associate with podocytopathy in type II diabetic patients | |
| IBRO Neuroscience Reports | Early mobilization in spinal cord injury promotes changes in microglial dynamics and recovery of motor function Pubmed:35586775 |
| Catalog No. | Related products for research use of Equus caballus; Equine (Horse) Organism species | Applications (RESEARCH USE ONLY!) |
| PAA037Eq01 | Polyclonal Antibody to Fibronectin (FN) | WB; IHC; ICC; IP. |
| SEA037Eq | ELISA Kit for Fibronectin (FN) | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Antigen Detection. |
| LMA037Eq | Multiplex Assay Kit for Fibronectin (FN) ,etc. by FLIA (Flow Luminescence Immunoassay) | FLIA Kit for Antigen Detection. |