Active Growth Arrest Specific Protein 6 (GAS6)
AXLLG; AXSF; AXL Stimulatory Factor; AXL receptor tyrosine kinase ligand
- Product No.APA204Hu01
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- Buffer Formulation20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl, pH8.0, containing 1mM EDTA, 1mM DTT, 0.01% SKL, 5% Trehalose and Proclin300.
- Traits Freeze-dried powder
- Purity> 90%
- Isoelectric Point5.6
- ApplicationsCell culture; Activity Assays.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 10µg50µg 200µg 1mg 5mg
- FOB
US$ 294
US$ 736
US$ 1472
US$ 4416
US$ 11040
For more details, please contact local distributors!
ACTIVITY TEST
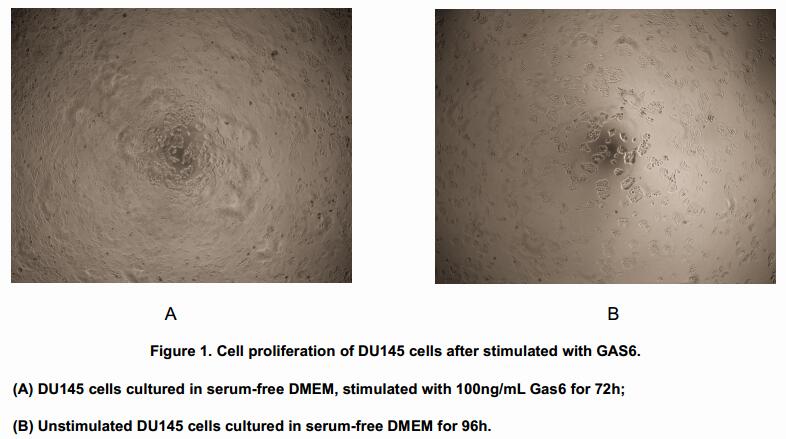
Growth arrest-specific 6, also known as GAS6, is a gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla) domain-containing protein thought to be involved in the stimulation of cell proliferation. It has been reported that both PC-3 and DU 145 human prostate cancer cell lines are stimulated to proliferate by Gas6, however, this proliferative response strictly correlates with the expression of the Axl receptor, being higher in DU 145 cells. To test the proliferative effect of Gas6, DU 145 cells were seeded into triplicate wells of 96-well plates at a density of 2,000 cells/well and allowed to attach overnight, then the medium was replaced with serum-free standard DMEM prior to the addition of various concentrations of GAS6. After incubated for 72h, cells were observed by inverted microscope and cell proliferation was measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Briefly, 10µL of CCK-8 solution was added to each well of the plate, then measure the absorbance at 450nm using a microplate reader after incubating the plate for 1-4 hours at 37oC.
Cell proliferation of DU145 cells after incubation with GAS6 for 72h observed by inverted microscope was shown in Figure 1.
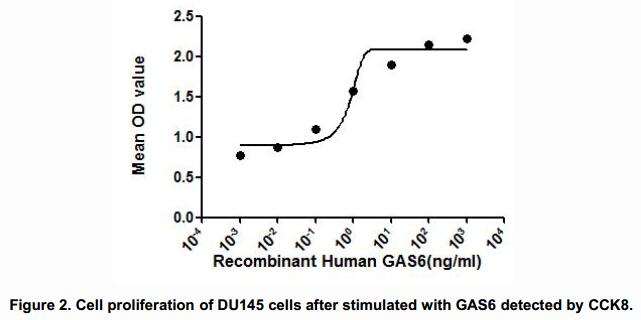
The dose-effect curve of GAS6 was shown in Figure 2. It was obvious that GAS6 significantly promoted cell proliferation of DU145 cells. The ED50 for this effect is typically 0.77~38.08ng/mL.
USAGE
Reconstitute in 20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl (PH8.0) to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL. Do not vortex.
STORAGE
Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Store at 2-8°C for one month. Aliquot and store at -80°C for 12 months.
STABILITY
The thermal stability is described by the loss rate. The loss rate was determined by accelerated thermal degradation test, that is, incubate the protein at 37°C for 48h, and no obvious degradation and precipitation were observed. The loss rate is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 BCA Protein Quantification Kit
BCA Protein Quantification Kit
-
 Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
Molecular Mass Marker for Protein
-
 Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
Monoclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
Polyclonal Antibody Customized Service
-
 Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
Protein Activity Test Experiment Service
-
 Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) Experiment Service
-
 Buffer
Buffer
-
 Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
Lentivirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
Adenovirus Packaging Experiment Service
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
Spike RBD Protein (S-RBD)
-
 Protein G
Protein G
-
 Protein A
Protein A
| Magazine | Citations |
| Acta Pharmacol Sin. | Pharmacological evidence: a new therapeutic approach to the treatment of chronic heart failure through SUR2B/Kir6.1 channel in endothelial cells. pubmed:27890915 |
| Frontiers of Medicine | The effects of Parenteral K1 administration in Pseudoxanthoma elasticum Patients Versus controls. a Pilot study Pubmed:29713628 |
| Oncotarget | DAPK and CIP2A are involved in GAS6/AXL-mediated Schwann cell proliferation in a rat model of bilateral cavernous nerve injury Pubmed:29464081 |
| journal of nutritional biochemistry | Gamma-glutamyl carboxylated Gas6 mediates the beneficial effect of vitamin K on lowering hyperlipidemia via regulating the AMPK/SREBP1/PPARα signaling … Pubmed: 31226525 |
| CELL DEATH AND DIFFERENTIATION | KPNB1-mediated nuclear translocation of PD-L1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation via the Gas6/MerTK signaling pathway Pubmed: 33139930 |
| 重度子痫前期患者血清GAS6 与其他炎症因子的相关性研究 | |
| JOURNAL OF NUTRITIONAL BIOCHEMISTRY | Gamma-glutamyl carboxylated Gas6 facilitates the prophylactic effect of vitamin K in inhibiting hyperlipidemia-associated inflammatory pathophysiology via arresting MCP-1/ICAM-1 mediated monocyte-hepatocyte adhesion 33789149 |