Packages (Simulation)

Reagent Preparation
Image (I)
Image (II)
Certificate


ELISA Kit for Collagen Type I Alpha 1 (COL1a1)
COL-1A1; COL1-A1; COL1A-1; OI4; Collagen Alpha-1(I)chain
- Product No.SEA350Hu
- Organism SpeciesHomo sapiens (Human) Same name, Different species.
- Sample Typeserum, plasma and other biological fluids
- Test MethodDouble-antibody Sandwich
- Assay Length3h
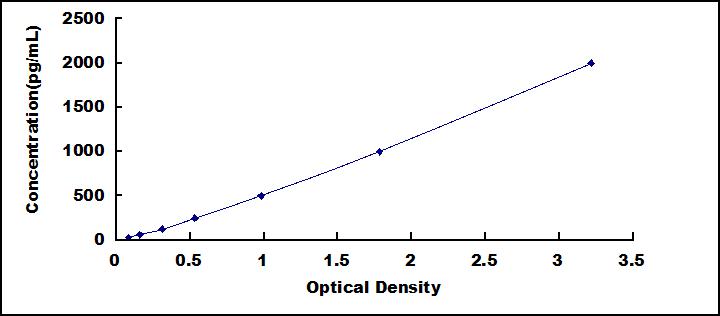
- Detection Range31.2-2,000pg/mL
- SensitivityThe minimum detectable dose of this kit is typically less than 12.4pg/mL.
- DownloadInstruction Manual
- UOM 48T96T 96T*5 96T*10 96T*100
- FOB
US$ 441
US$ 630
US$ 2835
US$ 5355
US$ 44100
For more details, please contact local distributors!
Specificity
This assay has high sensitivity and excellent specificity for detection of Collagen Type I Alpha 1 (COL1a1).
No significant cross-reactivity or interference between Collagen Type I Alpha 1 (COL1a1) and analogues was observed.
Recovery
Matrices listed below were spiked with certain level of recombinant Collagen Type I Alpha 1 (COL1a1) and the recovery rates were calculated by comparing the measured value to the expected amount of Collagen Type I Alpha 1 (COL1a1) in samples.
| Matrix | Recovery range (%) | Average(%) |
| serum(n=5) | 86-97 | 90 |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 83-94 | 88 |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 97-105 | 102 |
Precision
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Collagen Type I Alpha 1 (COL1a1) were tested 20 times on one plate, respectively.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): 3 samples with low, middle and high level Collagen Type I Alpha 1 (COL1a1) were tested on 3 different plates, 8 replicates in each plate.
CV(%) = SD/meanX100
Intra-Assay: CV<10%
Inter-Assay: CV<12%
Linearity
The linearity of the kit was assayed by testing samples spiked with appropriate concentration of Collagen Type I Alpha 1 (COL1a1) and their serial dilutions. The results were demonstrated by the percentage of calculated concentration to the expected.
| Sample | 1:2 | 1:4 | 1:8 | 1:16 |
| serum(n=5) | 95-105% | 89-97% | 96-103% | 82-102% |
| EDTA plasma(n=5) | 93-101% | 91-101% | 90-101% | 98-105% |
| heparin plasma(n=5) | 87-95% | 96-104% | 88-96% | 90-99% |
Stability
The stability of kit is determined by the loss rate of activity. The loss rate of this kit is less than 5% within the expiration date under appropriate storage condition.
To minimize extra influence on the performance, operation procedures and lab conditions, especially room temperature, air humidity, incubator temperature should be strictly controlled. It is also strongly suggested that the whole assay is performed by the same operator from the beginning to the end.
Reagents and materials provided
| Reagents | Quantity | Reagents | Quantity |
| Pre-coated, ready to use 96-well strip plate | 1 | Plate sealer for 96 wells | 4 |
| Standard | 2 | Standard Diluent | 1×20mL |
| Detection Reagent A | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent A | 1×12mL |
| Detection Reagent B | 1×120µL | Assay Diluent B | 1×12mL |
| TMB Substrate | 1×9mL | Stop Solution | 1×6mL |
| Wash Buffer (30 × concentrate) | 1×20mL | Instruction manual | 1 |
Assay procedure summary
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards;
2. Add 100µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 1 hours at 37°C;
3. Aspirate and add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent A. Incubate 1 hour at 37°C;
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times;
5. Add 100µL prepared Detection Reagent B. Incubate 30 minutes at 37°C;
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times;
7. Add 90µL Substrate Solution. Incubate 10-20 minutes at 37°C;
8. Add 50µL Stop Solution. Read at 450nm immediately.
GIVEAWAYS
INCREMENT SERVICES
-
 Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
Single-component Reagents of Assay Kit
-
 Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
Lysis Buffer Specific for ELISA / CLIA
-
 Quality Control of Kit
Quality Control of Kit
-
 ELISA Kit Customized Service
ELISA Kit Customized Service
-
 Disease Model Customized Service
Disease Model Customized Service
-
 Serums Customized Service
Serums Customized Service
-
 TGFB1 Activation Reagent
TGFB1 Activation Reagent
-
 Real Time PCR Experimental Service
Real Time PCR Experimental Service
-
 Streptavidin
Streptavidin
-
 Fast blue Protein Stain solution
Fast blue Protein Stain solution -
 Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
Single-component Reagents of FLIA Kit
-
 Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
Streptavidin-Agarose Beads
| Magazine | Citations |
| Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology and Endodontology | Simvastatin-loaded porous implant surfaces stimulate preosteoblasts differentiation: an in vitro study ScienceDirect: S1079210410004919 |
| Journal of Biomedical Materials | Osteoblast response to puerarin-loaded porous titanium surfaces: An in vitro study Wiley: source |
| European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology | Age effects on extracellular matrix production of vocal fold scar fibroblasts in rats Pubmed: 24077847 |
| J Voice. | Vocal Fold Fibroblast Response to Growth Factor Treatment is Age Dependent: Results From an In Vitro Study Pubmed: 24495429 |
| Arch Oral Biol. | Porphyromonas gingivalis LPS inhibits osteoblastic differentiation and promotes pro-inflammatory cytokine production in human periodontal ligament stem cells. Pubmed: 24370188 |
| Laryngoscope. | Establishing principles of macromolecular crowding for in vitro fibrosis research of the vocal fold lamina propria Pubmed:25545625 |
| UNIVERSA MEDICINA | Allogeneic human dermal fibroblasts are viable in peripheral blood mononuclear co-culture Univmed:Source |
| International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology | The vitamin D receptor agonist, calcipotriol, modulates fibrogenic pathways mitigating liver fibrosis in-vivo: An experimental study. pubmed:27477355 |
| National Natural Scientific | Role of Gut-Derived Endotoxin on Type I Collagen Production in the Rat Pancreas after Chronic Alcohol Exposure pubmed:29121396 |
| Nephron. | Prevention of Diabetic Nephropathy by Modified Acidic Fibroblast Growth Factor pubmed:28768285 |
| Cell and Tissue Research | Effect of TGFβ1, TGFβ3 and keratinocyte conditioned media on functional characteristics of dermal fibroblasts derived from reparative (Balb/c) and … Pubmed:29637306 |
| International Journal of Molecular Medicine | LOXL2, a copper-dependent monoamine oxidase, activates lung fibroblasts through the TGF-β/Smad pathway Pubmed: 30320382 |
| International Journal of Molecular Sciences | Association between Plasma HMGB-1 and Silicosis: A Case-Control Study Pubmed: 30558126 |
| Journal of Proteomics | Salivary proteins from dysplastic leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma and their potential for early detection Pubmed: 31706945 |
| Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences | Hesperidin inhibits the epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by transforming growth factor-β1 in A549 cells through Smad signaling in the cytoplasm |
| Ceramics International | Platinum nanoparticles supported on functionalized hydroxyapatite: Anti-oxidant properties and bone cells response |
| Scientific reports | Inhibition of eEF2K synergizes with glutaminase inhibitors or 4EBP1 depletion to suppress growth of triple-negative breast cancer cells 33911160 |
| Int J Mol Sci | Antiosteoporotic Nanohydroxyapatite Zoledronate Scaffold Seeded with Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Bone Regeneration: A 3D In Vitro Model Pubmed:35682677 |